Transparent and periodic boundaries¶
Learning targets
- Specify different conditions at different boundaries of the computational domain
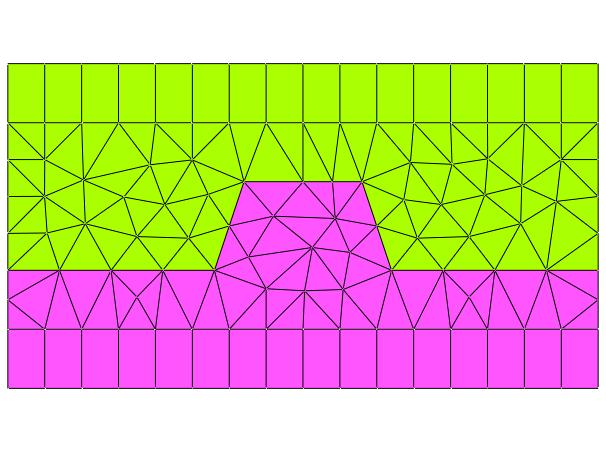
This geometry example specifies a rectangular computational domain with periodic boundaries at the left and right side of the computational domain and transparent boundaries at the upper and lower side of the computational domain. This is a typical situation for light scattering simulations with periodic scattering objects (e.g., diffraction grating). The resulting geometry and mesh correspond to the following figure:
.jcm Input File
layout.jcm [ASCII]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
Layout2D { Name = "GeometryTutorial2D/Grating" UnitOfLength = 1e-06 MeshOptions { MinimumMeshAngle = 20 MaximumSideLength = 1.2 } Objects { Polygon { Name = "ComputationalDomain/Background" DomainId = 1 Priority = -1 Points = [-5 -1, 5 -1, 5 2.5, -5 2.5] Boundary { Number = [1 3] Class = Transparent } Boundary { Number = [2 4] Class = Periodic } } Polygon { Name = "DielectricMaterial" DomainId = 2 Priority = 1 Points = [5 -1, 5 0, 1.5 0, 1 1.5, -1 1.5, -1.5 0, -5 0, -5 -1] } } }